Since 1989, the Center for Sport Nutrition at the National
Sports Institute of Malaysia (Institut Sukan Negara Malaysia) has
expanded its roles and functions in terms of providing appropriate nutritional
advice to athletes. Nutrition is very important to every athlete. All athletes
from different sports require dissimilar energy and nutrients based on their
respective sports. Here are the roles and responsibilities of sport dietitians:
 |
| Kosmo newspaper, 2009 |
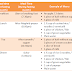
Roles
- Conduct comprehensive nutrition assessment and consultation.
- Educate in food selection, purchasing, and preparation.
- Provide medical nutrition therapy in private practice, health care, and sports settings.
- Identify and treat nutritional issues that influence health and performance.
- Address energy balance and weight management issues.
- Address nutritional challenges to performance (such as; gastrointestinal disturbances, iron depletion, eating disorders, female athlete triad, food allergies, and supplement use).
- Track and document measurable outcomes of nutrition services.
- Promote wound and injury healing.
- Oversee menu planning and design, including pre- and postevent and travel.
- Develop and oversee nutrition polices and procedures.
- Evaluate the scientific literature and provide evidence-based assessment and application.
- Work well with other health care providers.
Responsibilities
- Apply sports nutrition science to fueling fitness and performance.
- Develop personalized nutrition and hydration strategies.
- Advise on dietary supplements, ergogenic aids, meal and fluid replacement products, sports drinks, bars, and gels.
- Evaluate dietary supplements and sports foods for legality, safety, and efficacy.
- Provide nutrition strategies to delay fatigue during exercise and speed recovery from training.
- Help enhance athletic training capacity and performance.
- Participate in identifying and treating disordered eating patterns.
- Provide nutrition strategies to reduce risk of illness/injury and facilitate recovery.
- Promote career longevity for collegiate and professional athlete and all active individuals.
- Recruit and retain clients and athletes in practice.
- Provide sports nutrition as member of multidisciplinary/medical/health care teams.
- Provide reimbursable services (diabetes medical nutrition therapy).
- Design and conduct sports team education.
- Serve as a mentor for developing sports dietetics professionals
- Maintain credential(s) by actively engaging in profession-specific continuing education activities.
Reference:
American Dietetic Association. (2009). Position of the American Dietetic Association, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and Athletic Performance. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 109(3), 509–527. doi:10.1016/j.jada.2009.01.005
American Dietetic Association. (2009). Position of the American Dietetic Association, Dietitians of Canada, and the American College of Sports Medicine: Nutrition and Athletic Performance. Journal of the American Dietetic Association, 109(3), 509–527. doi:10.1016/j.jada.2009.01.005









0 comments:
Post a Comment